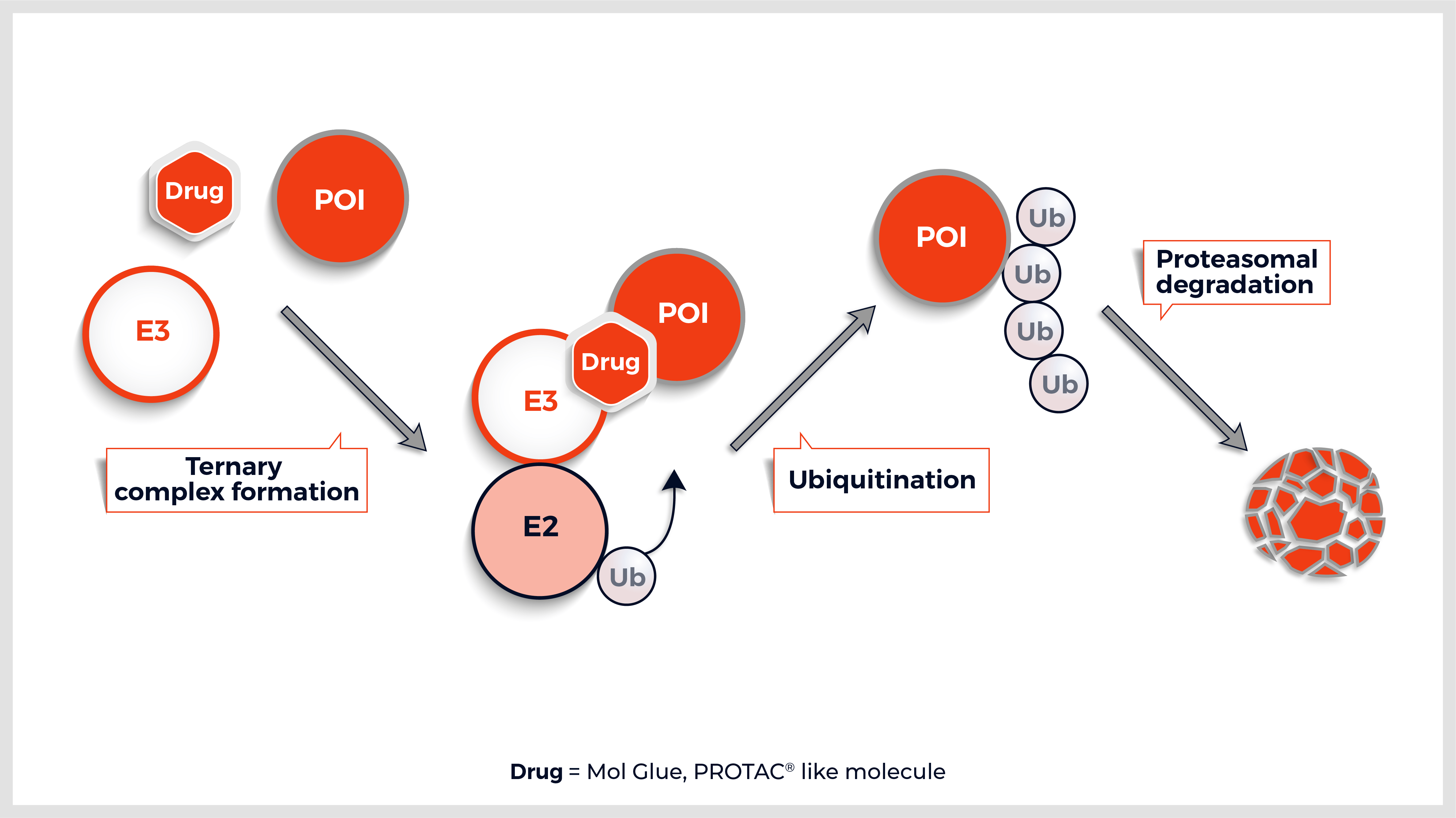
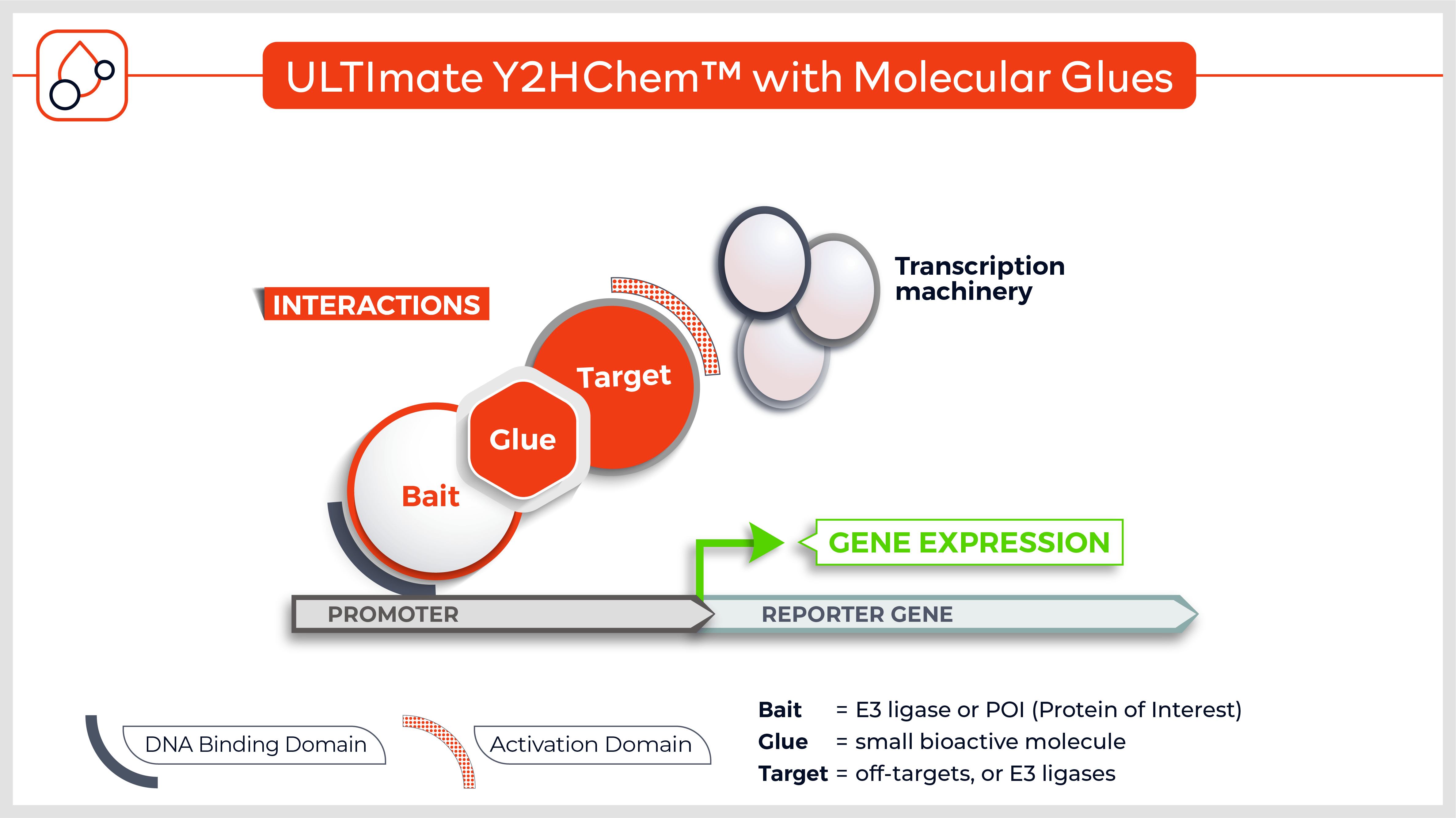
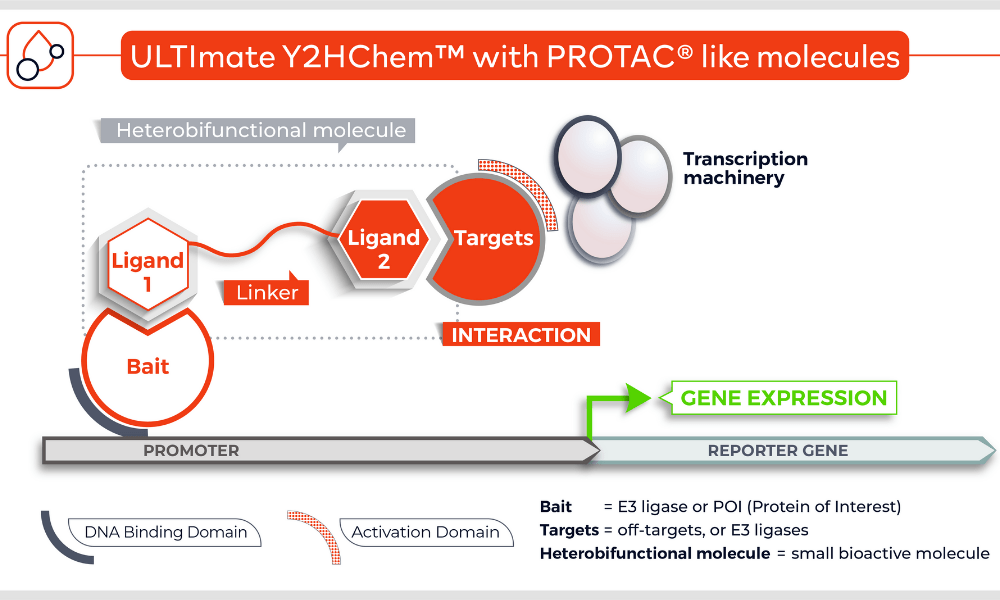
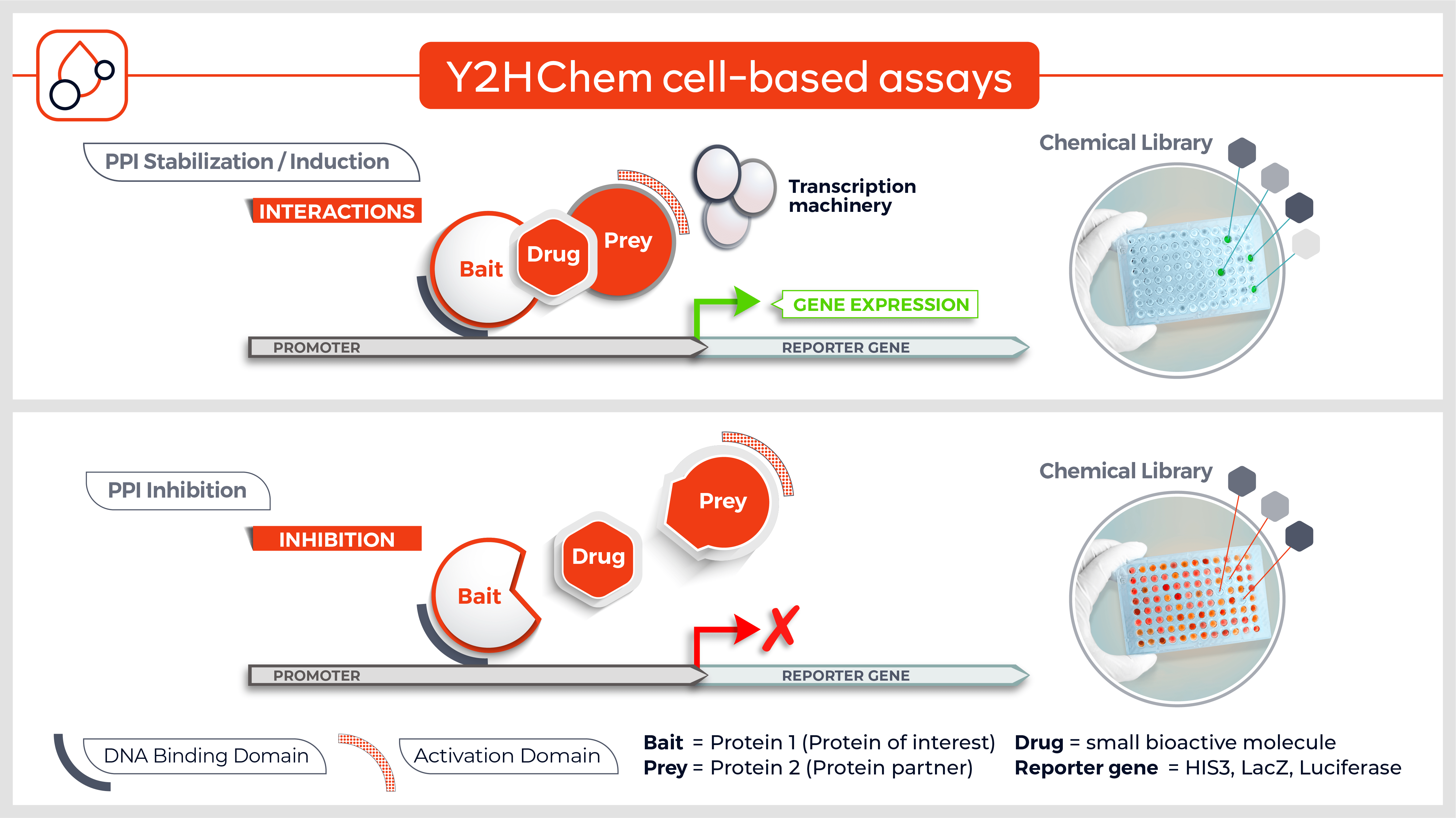
The Y2HChem relies on the reconstitution of a functional transcription factor (TF) followed by the expression of a reporter gene in genetically modified yeast cells. Upon a small molecule-induced PPI (mono or bivalent molecule), the DNA Binding Domain (DBD) of the TF is brought in close proximity to its Activation Domain (AD). This activates the transcription of the HIS3 reporter gene, allowing yeast cells to grow on selective medium lacking histidine.
The technique involves 3 components:
- Your protein of interest fused to the DBD
- Target proteins (fragment) fused to the transcriptional AD (the library)
- A small molecule